The next headings contain facts on vital components for selection and proper use of gearbox.
For certain information around the gearbox selection,see the related chapters.
1.0 OUTPUT TORQUE
one.one Rated output torque
Mn2 [Nm]
The torque that could be transmitted constantly as a result of the output shaft, together with the gear unit operated under a support factor fs = 1.
1.2 Necessary torque
Mr2 [Nm]
The torque demand based mostly on application requirement. It’s advised for being equal to or much less than torque Mn2 the gearbox under research is rated for.
one.3 Calculated torque
Mc2 [Nm]
Computational torque value to become used when deciding on the gearbox.
It is actually calculated looking at the demanded torque Mr2 and support issue fs, as per the connection right here following:Mc2 = Mr2 ?¡è fs ?¨¹ Mn2
two.0 Energy
two.one Rated input electrical power
Pn1 [kW]
The parameter is often discovered while in the gearbox rating charts and represents the KW that will be safely transmitted on the gearbox, based mostly on input speed n1 and support component fs= 1.
2.two Rated output electrical power
Pn2 [kW]
This worth may be the electrical power transmitted at gearbox output. it may be calculated using the following formulas:
Pn2 = Pn1 ?¡è |?d
Pn2= Mn2*n2/9550
three.0 EFFICIENCY
Efficiency can be a parameter which includes a key influence to the sizing of particular applications, and in essence relies on gear pair designelements. The mesh information table on page 9 shows dynamic efficiency (n1=1400)and static efficiency values.
Don’t forget that these values are only attained after the unit continues to be run in and is in the doing work temperature.
3.1 Dynamic efficiency
[|?d]
The dynamic efficiency will be the connection of electrical power delivered at output shaft P2 to electrical power applied at input shaft P1:
|?d =P2/P1
3.2 Static efficiency[|?s]
Efficiency obtained at start-up in the gearbox. Though that is typically not significant aspect for helical gears, it may be rather crucial when deciding on worm gearmotors working under intermittent duty.
four.0 Support Component
The service aspect (fs ) depends upon the operating problems the gearbox is subjected to your parameters that must be taken into consideration to select the most adequate servies element correctly comprise:
1. type of load in the operated machine : A – B – C
2. length of daily operating time: hours/day(?¡Â)
three. start-up frequency: starts/hour (*)
Style of LOAD: A – uniform,fa?¨¹0.3
B – moderate shocks, fa?¨¹3
C – hefty shocks, fa?¨¹10
fa=Je/Jm
–Je(kgm2) moment on the external inertia reduced on the drive shaft
–Jm(kgm2) moment of inertia of motor
–If fa>10 please make contact with our Technical Service
A -Screw 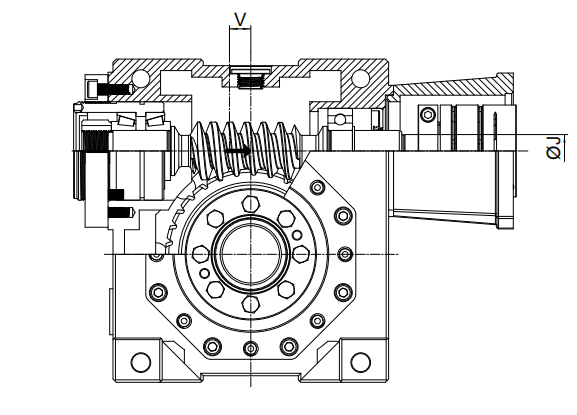 feeders for light supplies, fans, assembly lines, conveyor belts for light resources, little mixers, lifts, cleansing machines, fillers, manage machines.
feeders for light supplies, fans, assembly lines, conveyor belts for light resources, little mixers, lifts, cleansing machines, fillers, manage machines.
B -Winding units, woodworking machine feeders, items lifts, balancers,threading machines, medium mixers, conveyor belts for hefty elements,winches, sliding doors, fertilizer scrapers, packing machines, concrete mixers, crane mechanisms, milling cutters, folding machines, gear pumps.
C -Mixers for heavy components, shears, presses, centrifuges, rotating supports, winches and lifts for hefty resources, grinding lathes, stone mills, bucket elevators, drilling machines, hammer mills, cam presses, folding machines, turntables, tumbling barrels, vibrators, shredders.